Empowering U.S. Homes and Small Businesses
 In recent years, increasing climate volatility has had a significant impact globally. The United States has also experienced a range of natural disasters, including frequent solar flares and cyclones. In response, there has been a growing emphasis on transitioning to green and sustainable energy sources. Among these, solar power has emerged as a key focus area, with both residential and commercial sectors across the U.S. increasingly adopting solar energy systems to enhance resilience and support climate mitigation efforts.
In recent years, increasing climate volatility has had a significant impact globally. The United States has also experienced a range of natural disasters, including frequent solar flares and cyclones. In response, there has been a growing emphasis on transitioning to green and sustainable energy sources. Among these, solar power has emerged as a key focus area, with both residential and commercial sectors across the U.S. increasingly adopting solar energy systems to enhance resilience and support climate mitigation efforts.
Additionally, disruptions in the U.S. electrical grid have been on the rise as the infrastructure ages. To address these challenges and promote sustainable energy solutions, rooftop photovoltaic (PV) systems combined with on-site battery storage offers a highly effective approach for enhancing local resilience in residential and small business settings. This integrated solar-plus-storage system ensures uninterrupted access to clean energy, reduces reliance on the centralized grid, lowers electricity costs, and provides a critical backup power source during grid outages.
Why is resiliency important for homes and small businesses?
In recent years, several high impact 'black swan' events in the U.S. have exposed the vulnerabilities of centralized infrastructure. Notable examples include:
- California’s Public Safety Power Shutoffs (PSPS) in 2019, which left over two million customers without power during wildfire conditions.
- Winter Storm Uri in Texas (2021), which caused prolonged outages disrupting heating, water supply, and commercial activity.
- A rise in Atlantic hurricanes, which has consistently overwhelmed coastal grid systems.
These events significantly affected households and small businesses. However, those equipped with rooftop solar arrays and battery backup systems experienced minimal disruption, maintaining access to reliable power for essential needs.
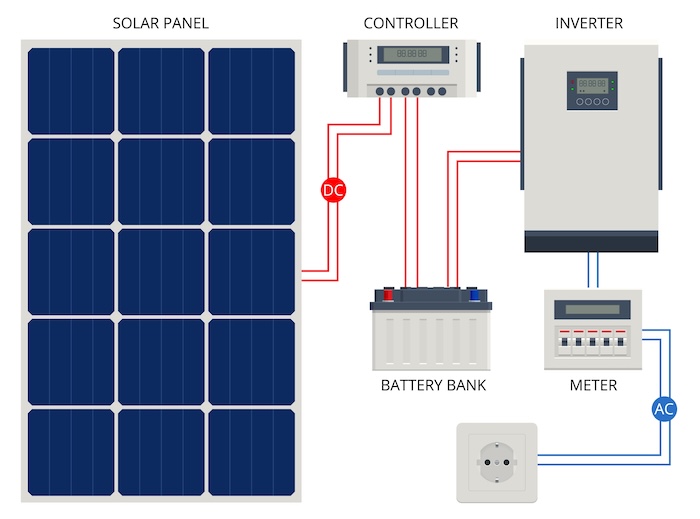
What components are required?
A typical solar-plus-storage system for residential and small commercial applications comprises many key components:
- High-efficiency photovoltaic (PV) solar modules, with bifacial monocrystalline panels are preferred due to their superior performance, achieving efficiency levels exceeding 22 percent.
- Battery storage systems, primarily using lithium-ion technology that offer enhanced safety, a long cycle life (6,000+ charge-discharge cycles), and a high depth-of-discharge range of 80–100 percent.
- Inverters or hybrid inverters, which convert direct current (DC) generated by the PV panels into alternating current (AC) for household or business use. Hybrid inverters are especially advantageous as they enable seamless transition to off-grid operation during power outages without the need for manual transfer switches.
- Energy management systems (EMS), which intelligently monitor and optimize energy generation, storage, and consumption. AI-driven EMS platforms are increasingly favored for their ability to enhance system efficiency and user control.
For a typical household or small business in the U.S., a system sized at 7–10 kW of PV capacity paired with 10–20 kWh of battery storage can provide 12 to 36 hours of autonomous operation — adequate to meet average daily energy demands during grid interruptions.
What will drive the adoption of solar + battery in the US?
The adoption of solar-plus-battery storage systems among residential and small commercial users in the U.S. has seen substantial growth over the past five years. The installation of residential solar peaked to 6.8 GW in 2023 from 2.3 GW in 2019, which reduced to 4.7 GW in 2024. In recent years, there has been significant growth in the deployment of solar + storage by residential and small businesses across the US.
Several key factors are driving this increased adoption of solar-plus-storage systems:
- Grid reliability concerns: Frequent extreme weather events (wildfires, hurricanes, and winter storms) coupled with aging grid infrastructure have amplified the need for resilient, decentralized energy solutions.
- Rising electricity costs: California, New York, Hawaii, and Texas have seen significant increases in retail electricity rates, prompting consumers to seek cost-effective alternatives.
- Emphasis on sustainability and ESG goals: Both households and businesses align with ESG objectives, spurring investments in clean energy.
- Federal incentives: The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) has extended the 30 percent Investment Tax Credit (ITC) for solar systems and standalone energy storage through 2032, improving project economics and accessibility.
- Technological advancements and consumer awareness: Innovations in battery technologies and a growing public understanding of the benefits of distributed energy resources have contributed to adoption momentum.
Emerging technological trends are poised to accelerate this trajectory further. The commercialization of solid-state batteries promises higher energy density, improved safety, and long-lasting, light-weight storage solutions. Additionally, the integration of second-life electric vehicle (EV) batteries into stationary storage applications may reduce system costs by 30–40 percent, making solar-plus-storage systems even more affordable and scalable for wider adoption.

Why is adoption still slow?
Despite the growing momentum, the widespread adoption of solar-plus-battery systems in the U.S. continues to face several challenges, including:
- High upfront costs
Energy storage systems remain expensive, making them less accessible for low- to middle-income households.
- Permitting and grid interconnection delays
Regulatory bottlenecks and lengthy approval processes for interconnection with utility grids often slow down project timelines and discourage adoption.
- Skilled labor shortages
The limited availability of trained technicians and installers is impacting the installation of solar + storage systems.
- Policy uncertainty
Potential shifts in federal priorities, particularly under a new administration, could result in reduced policy support or rollback of clean energy incentives.
Concluding insights
Standalone solar systems have long been the norm for U.S. households and small businesses. However, growing climate-related disruptions have underscored the need for greater energy resilience. Solar panels alone are no longer sufficient — integrating battery storage is now essential to ensure uninterrupted power.
Advancements in solar and battery technologies, combined with supportive policies, are making solar + storage more accessible and appealing. Continued innovation and favorable regulations will further drive adoption, enabling homes and businesses to better withstand grid outages.
Dhirendra Mishra is Associate Vice President, Growth Advisory (Energy & Infrastructure), at Aranca, a management consulting firm that provides, business research, investment research, intellectual property research, and valuation services to global clients.
Aranca | www.aranca.com
Author: Dhirendra Mishra
Volume: 2025 July/August











.png?r=9286)
