VPP 2.0 – Trends in Efficient Grid Integration
A next generation of Virtual Power Plants has emerged in 2025, embodying trends which will require more efficient integration with utility grids. These trends span a wide range: VPPs that integrate EV charging and other new resources; building management systems aggregated as VPPs; new use cases ranging from grid connected residential HVAC to AI-driven data centers; Community Choice Aggregators that are integrating VPP’s as they begin to act as demand response aggregators; and the emergence of solar panel manufacturers diversifying into VPP creation and management.
The scope of resources being aggregated by VPPs continues to broaden well beyond the earlier generation of rooftop solar resources. In a great example, managed EV charging providers are partnering or being acquired by leading rooftop solar aggregators and smart energy ecosystem providers, expanding the notion of what constitutes a Virtual Power Plant. This kind of partnership adds charging stations and the electric vehicles themselves to a pool of distributed energy resources, alongside photovoltaics and the fast-growing Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) market. In turn, the BESS market as a standalone distributed energy resource (DER) is rapidly developing in parallel with VPP innovations. A recent BESS market entrant based in the U.K. has demonstrated the growing European market for VPP and DER innovation.
The category of commercial building management systems is experiencing a renaissance, after having been a core part of the growth in the utility demand response market ten years ago. Recent solutions focus on more seamless integration between grid-interactive efficient commercial buildings and utility operations. One company installs a gateway, incorporating a small yet powerful edge computer, in a building’s server room and connects to the controls network. The gateway identifies all connected devices using standard building OT network protocols like BACnet and Modbus. It then maps and classifies devices using a combination of artificial intelligence (AI) and manual categorization to enable data model which leverages trend data at 1 min to 15 min intervals, much more granular than first-generation utility time-of-use programs
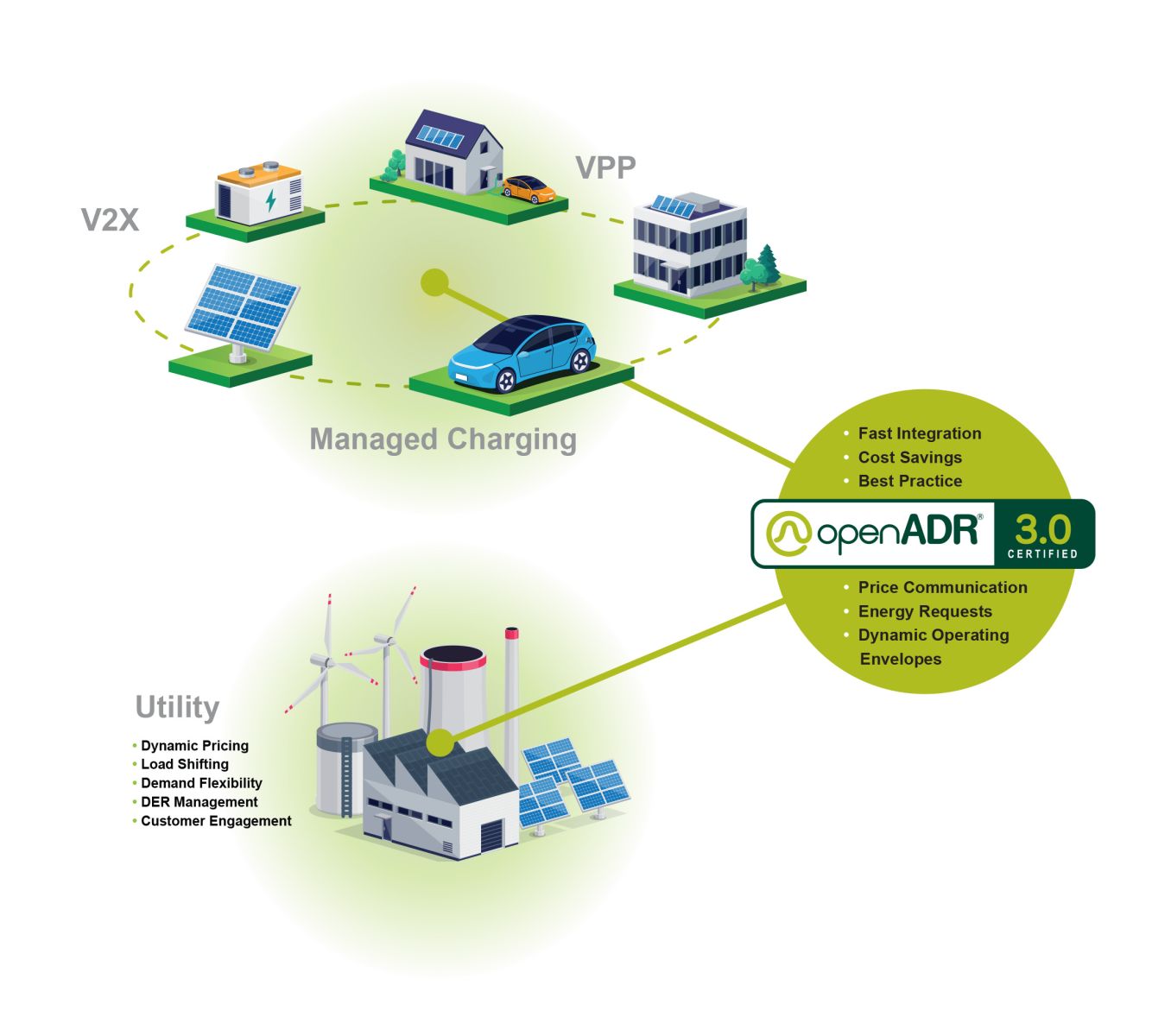
In the wake of the compensation rule changes for Community Choice Aggregators in California in 2023, a reorganization of the VPP provider market is starting to take shape. A new VPP project funded by the U.S. Department of Energy is planning to leverage its status as a Community Choice Aggregator (CCA) — and its work as a load-serving entity (LSE), scheduling coordinator, and registered Demand Response Provider (DRP) — to demonstrate how CCAs can use Virtual Power Plants to create new opportunities and value for the buildings they serve, while enhancing grid health and reliability. The project’s Concept Paper includes the following detail:
The team proposes to aggregate up to 12 MW of new and existing DERs at select commercial and industrial (C&I) sites to demonstrate innovative bi-directional demand response strategies using the Load Shift Resource (LSR) market-participation model that was recently added to the CAISO-FERC tariff. The LSR option allows dispatchable resources to bid load bi-directionally using two separate Resource IDs (load curtailment and load consumption). This bidirectional will unlock substantial value creation for all stakeholders. The project also leverages more conventional industry technology partners to deliver technical resources, distributed energy resources, and a detailed risk assessment and system analysis to ensure optimal and reliable outcomes for all stakeholders.
Many of the long-time solar panel manufacturers exhibiting at RE+ have been adding storage to their product portfolios, eyeing the utility market. Several of the top ten manufacturers in the U.S. market are now engaged in discussions as to how best they can connect and communicate directly with utilities as grid resources.

And in the last and possibly most momentous trend, a group of European and Asian partners have entered the U.S. market with a new set of solutions to the challenge of integrating renewable energy into utility grids. A few examples include:
- Transformation of various facilities and machines into virtual storage batteries, where buildings, facilities, machines, etc. become power resources.
- Management of various businesses engaged in renewable electricity provided at scale, including the development, operation, and management of renewable energy power plants such as solar, wind, and hydropower generation.
- Development of energy management systems encompassing solar and wind power integrated with energy storage battery systems.
- Integration of wholesale electricity purchases with non-fossil energy certificates to provide up to 100 percent green electricity to customers.
- Provision of a virtual power plant solution with a new type of photoelectric dispatch management and trading system.
- Development of a platform that will make it easier to adopt renewable energy (natural energy) as an alternative to non-renewable energy, integrating elements including PV modules, liquid flow batteries, and multi-function data collection equipment.
Virtual Power Plant providers are the newest and fastest growing market segment to join the existing installed base of flexibility providers, including demand response systems, smart thermostats, EV managed charging providers, building management systems and more.
Don Dulchinos is Director of Market Facilitation at the OpenADR Alliance, manager of an open, highly secure, and two-way information exchange model and global Smart Grid standard. OpenADR standardizes the message format used for Auto-DR and DER management so that dynamic price and reliability signals can be exchanged in a uniform and interoperable fashion among utilities, ISOs, and energy management and control systems. Don can be reached at [email protected].
OpenADR Alliance | www.openadr.org
Author: Don Dulchinos
Volume: 2025 September/October









