Achieving Grid Modernization Goals Through Value-based Decision Making
Grid modernization is having a profound impact on the nature and regulation of North American utilities. It represents a significant change to the way energy is managed, distributed, and used—today and in the future. As Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) targets become increasingly important to energy investors and regulators, how can organizations transform their Asset Investment Planning (AIP) processes to overcome challenges and take advantage of emerging opportunities?

Grid modernization
The energy transition refers to the global energy sector’s shift from fossil-based systems of energy production and consumption to renewable energy sources like wind and solar, as well as long-term energy storage such as batteries. The increasing penetration of renewable energy into the energy supply mix and the onset of electrification and improvements in energy storage are key drivers of the energy transition.
Grid modernization is a subset of the energy transition, and refers to changes needed in the electric transmission and distribution (T&D) systems to accommodate these rapid and innovative technological changes. Grid modernization often necessitates the increased application of sensors, computers, and communications to increase the intelligence of the grid and its ability to respond swiftly to external factors. The main goals of the grid are to provide the capacity, reliability, and flexibility needed to adapt to a whole range of new technologies (in the drive to net zero), while maintaining a comparable level of service and cost to the end customer.
Grid modernization projects are driven by both climate resilience through hardening of assets and changes to the T&D network to accommodate climate mitigation strategies. There are 3 broad categories for these types of projects:
- Climate Resilience and Infrastructure Hardening
- These investments cover physical improvements to T&D assets to reduce outages or damage, and enhanced system capabilities in the areas of flood resistance, storm hardening, wildfire risk mitigation, and cyber security.
- These investments cover physical improvements to T&D assets to reduce outages or damage, and enhanced system capabilities in the areas of flood resistance, storm hardening, wildfire risk mitigation, and cyber security.
- Smart Grid and Distribution System Modernization
- Projects in this area cover advanced grid technologies that enable two‐way communication, self‐healing, and autonomous restoration (using digital sensors and switches with advanced control and communication technologies). Advanced metering and communication infrastructure are also included in this category.
- Projects in this area cover advanced grid technologies that enable two‐way communication, self‐healing, and autonomous restoration (using digital sensors and switches with advanced control and communication technologies). Advanced metering and communication infrastructure are also included in this category.
- Distributed Energy Resource (DER) Optimization
- These projects cover grid modifications required to support the integration of resources such as microgrids, distributed solar, wind, and storage (hydrogen, battery), as well as the inclusion of electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure.
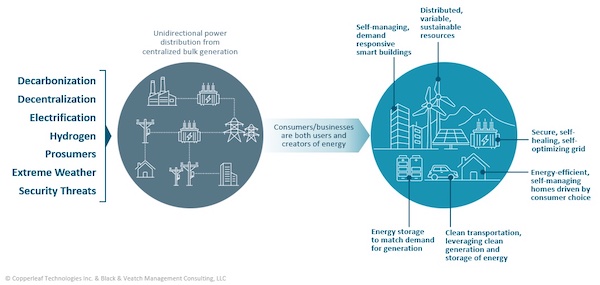
Grid modernization is accelerating due to multiple factors, such as decarbonization, electrification, extreme weather, and security threats.
Valuing innovative projects
The changing demands dictated by grid modernization will require organizations to strike the right balance between cost-effectively managing the current business, while investing appropriately to meet future demands. Organizations are already seeing an increase in both the volume and variety of grid modernization projects. This is leading to increased planning complexity, requiring utilities to demonstrate that they are spending their limited budgets and resources to maximize value and drive their ESG and performance targets.
A value-based approach to investment decision making is key to establishing a common basis to evaluate potential investment opportunities and meet the challenges of grid modernization. The key to achieving your organization’s grid modernization goals is building a multi-year plan that breaks the work into executable chunks. This ensures adequate funding and resources are available to carry out the plan in the short-term, resulting in incremental progress toward longer-term objectives.
With a value-based decision-making approach, organizations can ensure they are making the right grid modernization investments—and justify their plans to internal and external stakeholders.
Align decisions with strategic objectives
Business leaders must develop frameworks that quantify the financial and non-financial benefits of all proposed investments on a common scale and understand how projects will contribute to their short- and long-term grid modernization initiatives and broader energy transition goals. A value framework also creates a clear line of sight from planned investments to regulatory and corporate targets, allowing organizations to provide transparency into the decision-making methodology—and demonstrate the benefits of their plans to regulators, stakeholders, and customers:
 Russ is a Director of Product Management, Decision Analytics at Copperleaf. He is an innovative leader with over 20 years of comprehensive business and technical experience in high-tech product development organizations. Russ holds a B.A.Sc. in Mechanical Engineering from the University of British Columbia and a Management of Technology MBA from Simon Fraser University.
Russ is a Director of Product Management, Decision Analytics at Copperleaf. He is an innovative leader with over 20 years of comprehensive business and technical experience in high-tech product development organizations. Russ holds a B.A.Sc. in Mechanical Engineering from the University of British Columbia and a Management of Technology MBA from Simon Fraser University.
Copperleaf | www.copperleaf.com
Author: Russ Stothers








